Repositories
LDH Cytotoxicity Analysis App
A comprehensive R Shiny application to automate the analysis of LDH cytotoxicity assays. Features interactive plots, dynamic user controls for flexible data input, robust statistical analysis (ANOVA/Kruskal-Wallis), and downloadable reports.
Repo:LDHAAW
Status: Released
Implementation: R, Shiny
Key Packages: Tidyverse, ggiraph, ggpubr, rmarkdown
Master's Thesis Project
GOT STRUCTURE? Population Genetic Structure and Demographic History of Calanus hyperboreus
Nord University | M.Sc. Biosciences, Genomics | July 2024
Abstract
Calanus hyperboreus, a keystone zooplankton species in Arctic food webs, has been understudied due to challenges in sequencing its large, repetitive genome. This study utilized target capture sequencing (TCS) to investigate its population genetic structure. From an initial ~4.9 million SNPs, a filtered dataset of 389 SNPs from 54 individuals across 11 locations was analyzed. Population genetic analyses revealed high levels of gene flow, suggesting C. hyperboreus is a single panmictic population. However, pairwise FST comparisons detected subtle but statistically significant differentiation between certain locations. Demographic analyses (Tajima’s D, Site Frequency Spectrum) revealed a skew toward low-frequency variants, indicating a recent population expansion.
Key Findings & Visualizations
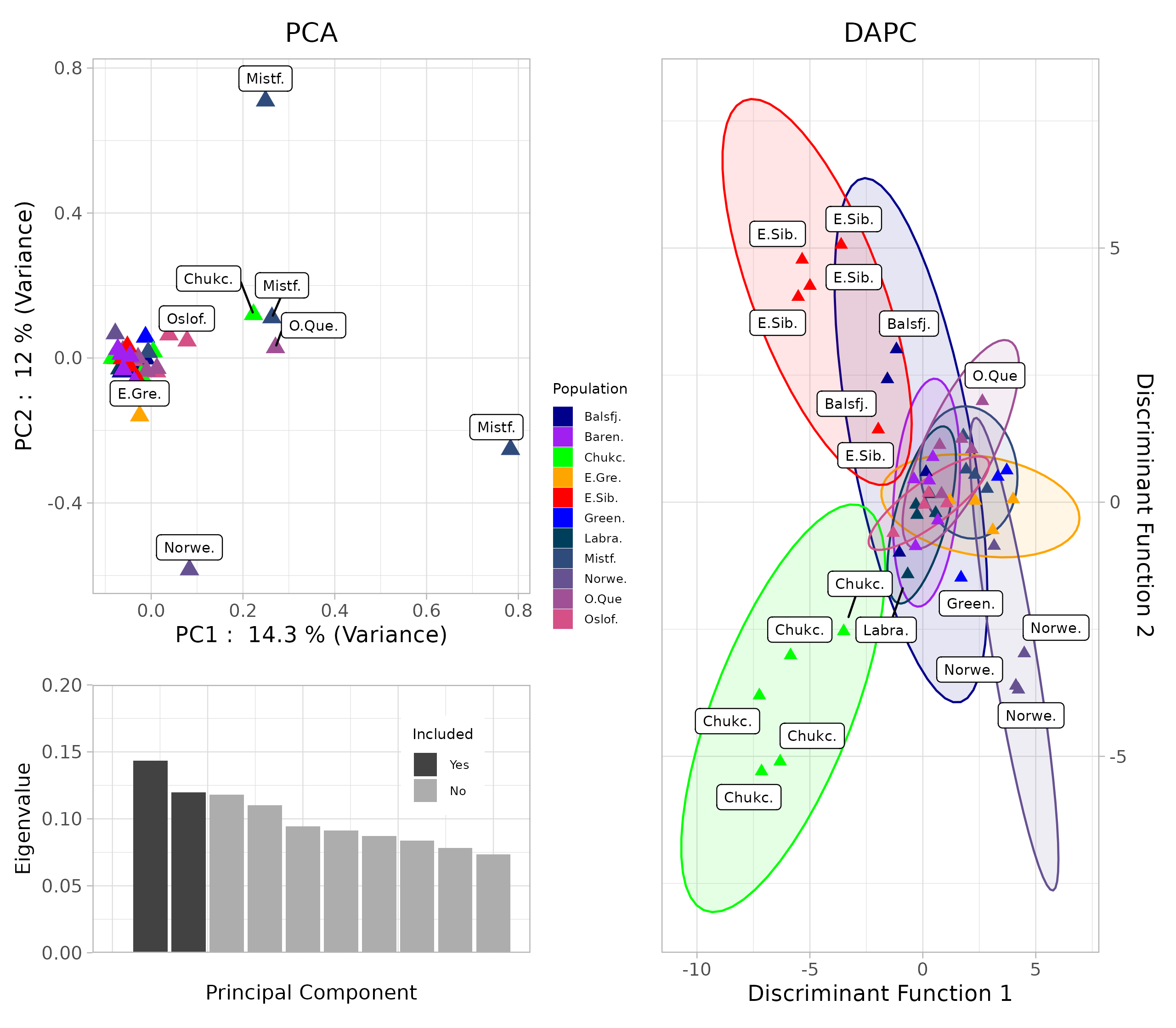
1. A Single Panmictic Population with Subtle Structure
Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and ADMIXTURE analysis did not reveal distinct genetic clusters corresponding to sampling locations, suggesting high gene flow. However, Discriminant Analysis of Principal Components (DAPC) and pairwise FST comparisons showed subtle clustering and statistically significant differentiation between some locations, particularly the Chukchi Sea samples.
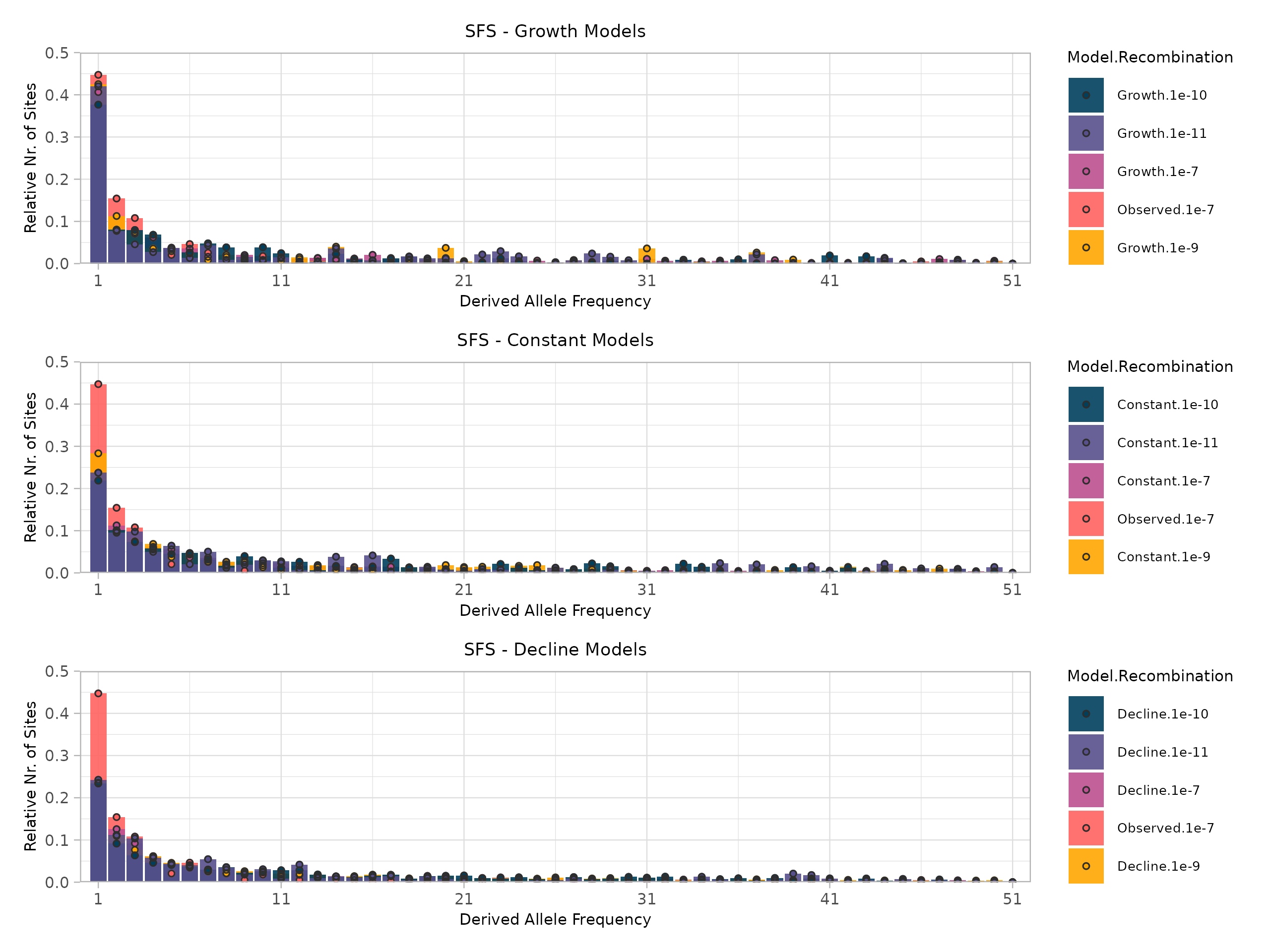
2. Evidence of Recent Population Expansion
The Site Frequency Spectrum (SFS) showed a significant excess of rare alleles (low-frequency variants), a classic signature of recent population expansion. This finding, supported by a negative overall Tajima's D value, suggests the species may have undergone a demographic expansion, possibly following the last glacial period, similar to its relative C. glacialis.
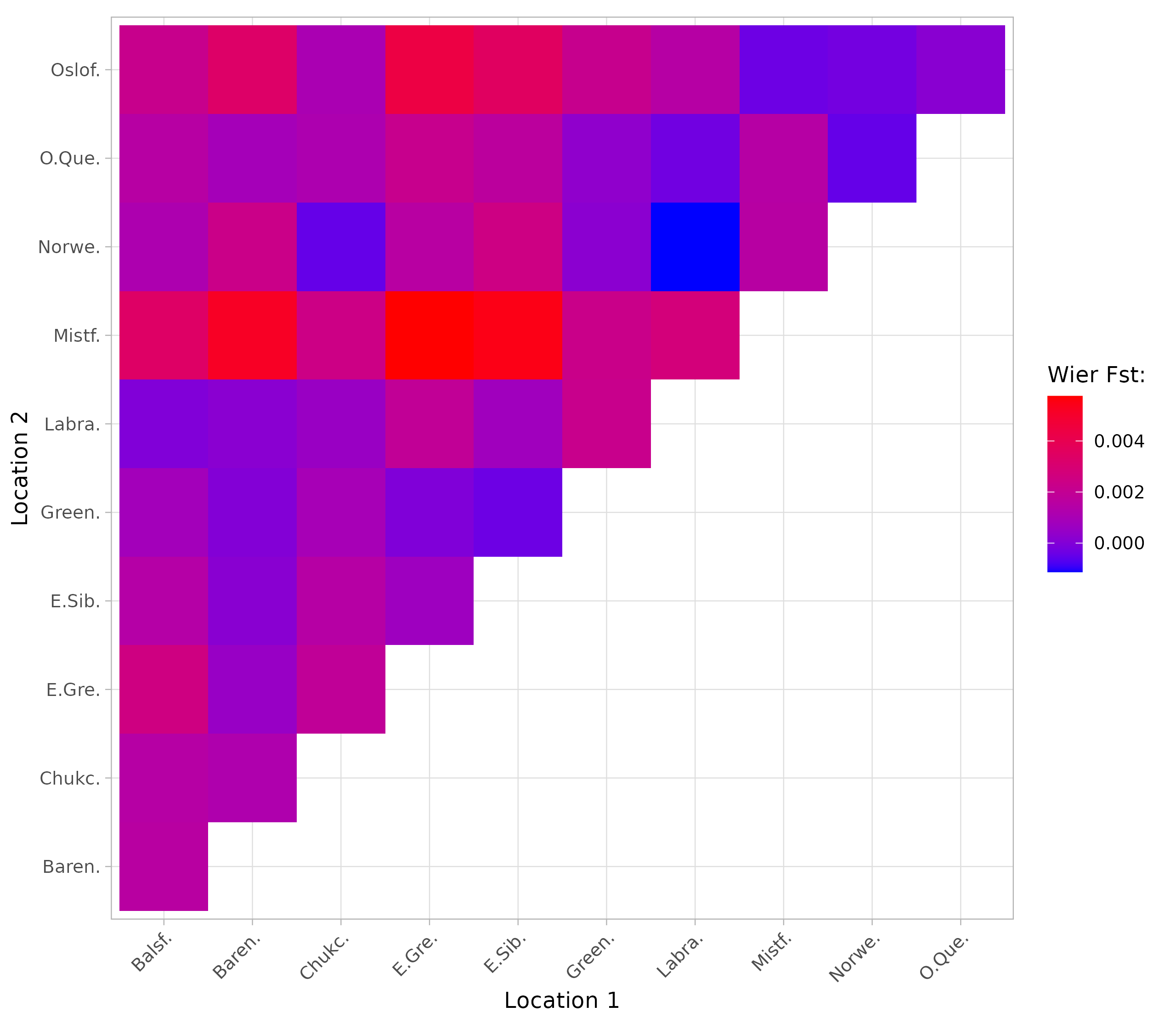
3. Low but Significant Pairwise Differentiation
While overall structure was weak, pairwise FST (Weir-Cockerham) comparisons revealed statistically significant, albeit low, levels of genetic differentiation between several sampling locations. This indicates that while gene flow is the dominant force, factors like geographic distance or local adaptation may contribute to minor divergence.